TIGHTEN, TONE & REPAIR YOUR WHOLE BODY
Support your Tendons, Ligaments, Muscle Tissues, Healthy Digestion and Glowing Skin with Collagen Protein
- Healthy gut repair and function
- Greater mobility and flexibility
- Strong, healthy muscles
- Healthier, stronger bones and joints
- Vibrant, firmer, glowing skin
- Easier weight management and/or weight loss, due to its satiating effect on hunger
- Fighting back against the effects of normal aging
- Deeper and more restful sleep
- Healthy brain function
Most people aren’t getting enough collagen from diet alone
Why Collagen is Essential for Health Restoration
Collagen is essential for your health and for my health. Here’s why.
Collagen is a protein made up from amino acids, including the amino acids proline, glycine, glutamine and arginine. In fact, collagen is so important that it makes up approximately 30 percent of all the proteins in the body, and is found all over the body—in tendons, ligaments, bones and much more. You might say that collagen is the “glue” that holds us together because it truly is.
Collagen is found only in animals, mostly in the flesh and connective tissue, and it’s the second most common substance in the body—second only to water. It’s well known for how it helps our skin maintain its firmness and smoothness and for how it supports the renewing of skin cells.
Many people try to improve their skin with lotions and potions from the outside, but my collagen protein can support healthy skin from the inside out. How cool is that? However, collagen’s benefits don’t stop there.
Likewise, collagen plays a big part in healthy nails and hair. It’s also involved in maintaining healthy tendons—tissues which attach muscles to bones—as well as in strong ligaments, a type of connective tissue which attaches bones together and thereby also holds joints together.
But that’s not all by any means. Additionally, collagen is found in the bones, blood vessels, the digestive tract, the heart, the cornea, the gallbladder, the kidneys, the bladder, smooth muscle tissues and in cartilage.
But wait. There’s more. Collagen is even cited as helping to reduce the appearance of cellulite.
Yes. It’s true. Cellulite is a result of fatty tissues pushing up through fibers in the skin’s upper layer, giving that recognizable dimpling associated with cellulite
Collagen may help to work against cellulite from the inside out, repairing and rebuilding those fibers that cause cellulite to show.
You see? When you or I have enough collagen in our bodies, then we are well put together and can hum along with our health. When collagen supplies dip, however, then we could be heading for trouble.
Aging has a way of lowering collagen levels, but you really don’t have to be that old for this to happen. The truth is that collagen production in the body slows starting around age 20. That’s right. 20! In fact, after the age of 20, one percent of collagen is produced in the skin each year. That shortfall can really add up over the years, too, causing all sorts of fallout.
When the body doesn’t have enough collagen, the skin starts to thin, wrinkle and sag. Hair gets lifeless or limp, and tendons and ligaments aren’t as elastic as they use to be. Your joints can feel it, too. They can get stiff and “creaky.”
However, supplementing with collagen can help boost collagen levels in the body to support healthy tendons, ligaments, joints, and skin. Additionally, collagen protein supplements may support better metabolism, boost energy levels and help to maintain healthy muscle tissue.
Announcing a Potent Blend of Collagen Powder
We’ve spent years developing a specific Multi-Collagen Protein formula. And — in conjunction with a healthy, low-inflammation diet — my multi-collagen protein powder can help support healthy skin, muscles, joints, gut, brain, weight and more. †
With our potent, high-quality blend of bovine, chicken, fish, and egg collagens, providing collagen types types I, II, III, V and X you’ll have everything you need to power a healthy you.†
Dr. Collagen’s Multi Collagen Protein contains:
Bovine Collagen
Bovine collagen is a naturally occurring protein found in the skin, bones and muscles of cows. This type of collagen is very similar to what we have in our bodies and provides a healthy dose of types I and III collagen.
Types I and III are the major components of skin, hair, nails, muscles, tendons, ligaments, bones, gums, teeth, eyes and blood vessels.
And together Types I and III collagen make up more than 90 percent of the collagen in our bodies.
Because it delivers a dense collagen punch to your cells, this is one of the most beneficial and effective ways to consume collagen.
Bovine collagen is also rich in the amino acid glycine, which is necessary for building healthy DNA and RNA strands. These are the essential genetic building blocks for properly functioning body cells. Glycine is also one of the three amino acids which form creatine. Creatine is known to support, promote healthy muscle growth, and aid in energy production during workouts.†
Last but not least, bovine collagen also provides the amino acid proline. Proline plays a critical role in the body’s ability to produce it’s own collagen.†
In addition to bovine collagen, Dr. Collagen’s Multi Collagen Protein also contains chicken collagen.
Chicken collagen
Chicken collagen is known as type II collagen, which is targeted for gut and joint health, immunity, and the body’s healthy inflammatory response. It’s a protein found in the cartilage, bones and other tissues of chickens.
It’s the most popular collagen product used in medicine. It’s also the major component of joint cartilage.
Chicken collagen is loaded with joint-healthy chondroitin sulfate and glucosamine sulfate—both of which are great for supporting your joints and maintaining healthy pH levels.†
Dr. Collagen’s Joint Support also contains fish collagen.
Fish collagen
Fish collagen contains Type I collagen. Due to their smaller size, the peptides from fish collagen are absorbed more easily through the intestinal barrier and into the bloodstream, where it is carried throughout the body.
As a result, it can support collagen synthesis in the joint tissues, bones and in the skin.
Fish collagen is also rich in the amino acids glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline. Hydroxyproline is a rare non-essential amino acid that naturally triggers collagen production and helps to promote the stability of collagen throughout the body. †
Egg Collagen
Egg collagen is abundant in egg whites and the egg shell membranes of hens. In fact, Egg shell membrane is rich in nutrients similar to types I and V collagen, glucosamine sulfate, chondroitin sulfate, hyaluronic acid and amino acids—all of which are beneficial for normal joint health and connective tissue health.†
Try Collagen to help improve your digestion, joints and glowing skin
Collagen does so much for the body and in the body to keep it healthy. It’s literally the “glue” that holds us together, so make sure you get enough of it. There’s no need for you or your health to fall apart.
Use Collagen Protein to restore, rebuild and replenish your entire body. You’re going to love how you feel when taking Collagen! So, try it today.
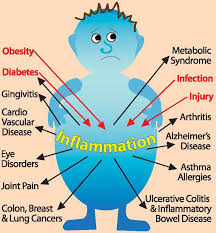

 Protein is a powerhouse of a macro nutritions
Protein is a powerhouse of a macro nutritions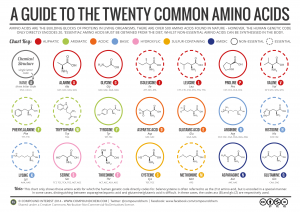 There are 20 amino acids.
There are 20 amino acids.









 Want a smart swap for a healthier dessert? You already know avocados are nutritional powerhouses, thanks to the fiber, B vitamins, folate, and
Want a smart swap for a healthier dessert? You already know avocados are nutritional powerhouses, thanks to the fiber, B vitamins, folate, and 




 Coconut oil has been demonized in the past because it contains saturated fat.
Coconut oil has been demonized in the past because it contains saturated fat.






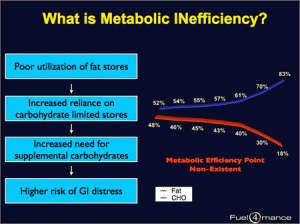 Coach BK and Bob Seehohar, author of the fantastic book, Metabolic Efficiency training chat why it is so important to become more FAT ADAPTED.
Coach BK and Bob Seehohar, author of the fantastic book, Metabolic Efficiency training chat why it is so important to become more FAT ADAPTED.