Endocrine System: very complex system that affects every other system in the body. This system is comprised of many glands which work together.
Webster says the endocrine system is the collection of endocrine glands that produce hormones that are used as chemical messengers throughout the body to help regulate vital processes including metabolism, growth, sleep, and reproduction.
Think: POST OFFICE. Mailman. Delivers important information where it’s suppose to.
Also think: DANCE. Between the hormones produced by the endocrine glands AND the receptor cells in the target organs. (lock and key)
Receptor cells are very sensitive and response to even the tiniest amount of hormone. The receptor cell then triggers a response/action/job/etc.
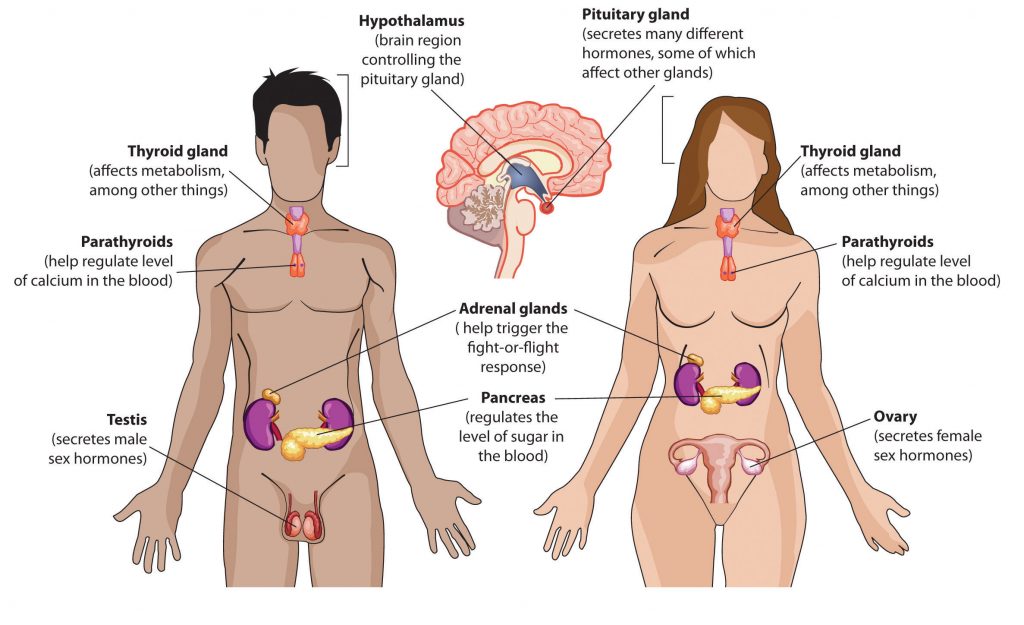
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM TEAM MEMBERS
- Pituitary Gland: Master gland. produces hormones that control the other members of the endocrine system. Base of the brain. Works with the hypothalamus. Comes in two parts and produces 8 different hormones. More on that later.
- Thyroid Gland: Regulate the body’s metabolism, produces energy.
- Parathyroid Glands: Regulate blood calcium levels. Has an influence on bones, muscle contractions.
- Thymus Gland: Part of the immune system, between the lungs. Largest before puberty, then stops working
- Adrenal Glands: Regulates the body’s response to stress, regulates body’s pH, heart rate, blood pressure, energy production, CO2 regulation
- Pancreas: Digestion, control blood sugar levels throughout the day
- Ovaries, in women: Sex hormones
- Testes, in men: Sex hormones
- Pineal: production of melatonin, the sleep hormone, which starts in the eye.
- Hypothalamus: link between the nervous system and the endocrine system. Neighbor of the pituitary gland. Gets cues from the nervous system, then produces neurohormones to tell the hypothalamus what hormones to produce to respond and control the body.
- Example: You are hot. You need to manage sodium, water, etc so your brain doesn’t melt when you are doing that last 13.1 hot run of Muncie 70.3.
Endocrine glands release their hormones directly into the body through the blood stream (diffusion) compared to other glands that release their hormones locally through ducts, which “stay and act” in that local area, such as sweat glands. Endocrine glands can have an impact on any part of the body through diffusion (blood stream).